Documentation
Board Revisions: 2.5.x — 2.6.x
(boards shipped in 2023)
Contents
Getting Started
So you've got your Sonatino — now what? Let's make some sound!
The easiest way to get up and running with Sonatino is to install the Arduino IDE and flash an example sketch to the board. To do that, follow the steps below:
- Download and install the Arduino IDE (version 2.0 or above).
- Install Arduino-ESP32 by referring to these instructions. Essentially, you need to add the following to "Additional boards manager URLs" (in Preferences):https://raw.githubusercontent.com/espressif/arduino-esp32/gh-pages/package_esp32_index.jsonAfter adding the URL, open the Boards Manager, search for "esp32", and install "esp32 by Espressif Systems".
Note: For compatibility with other libraries (including ESP8266Audio), it's recommend that you use version 2.x.x of the esp32 board package. Version 3 of the esp32 package is gaining support, but as of now, some libraries may not work with it as expected. - Install the ESP8266Audio library in the Arduino IDE (using the Library Manager or manually from here). This library is required for the example sketch to work.
- Download the Sonatino Examples and open v2.x.x/playback/playback.ino with the Arduino IDE.
- Make sure both level selection DIP switches on the board are set to the "ON" position (positioned to the right when the board is oriented as shown in the images in this documentation). They should be set to "ON" by default, but can be changed using a small screwdriver or paperclip.
- Plug Sonatino into your computer using a USB-C cable. If a green LED does not light up on the board, try a different USB port or cable.
- Within the Arduino IDE, select the port corresponding to the Sonatino board (will vary based on your system), and make sure the board is set to "ESP32S3 Dev Module". For the serial monitor to work, you'll also need to set "USB CDC on Boot" to "Enabled".
- Click the "Upload" button to compile the sketch and flash it to Sonatino.
If everything went well, you should see the blue LED begin to flash on the board, and if you plug in a pair of headphones you should hear music playing.
Board Overview
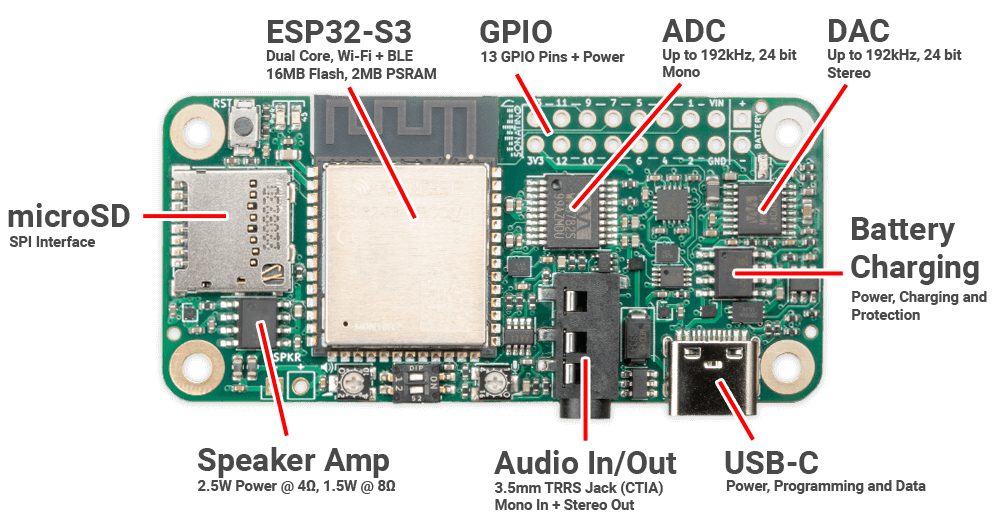
MAIN COMPONENTS
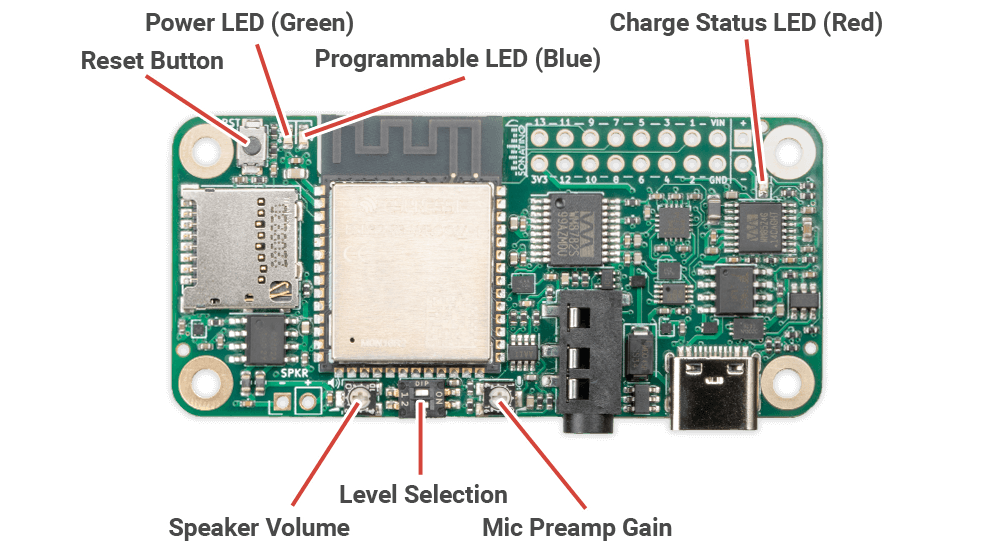
CONTROLS & INDICATORS
OPTIONAL COMPONENTS
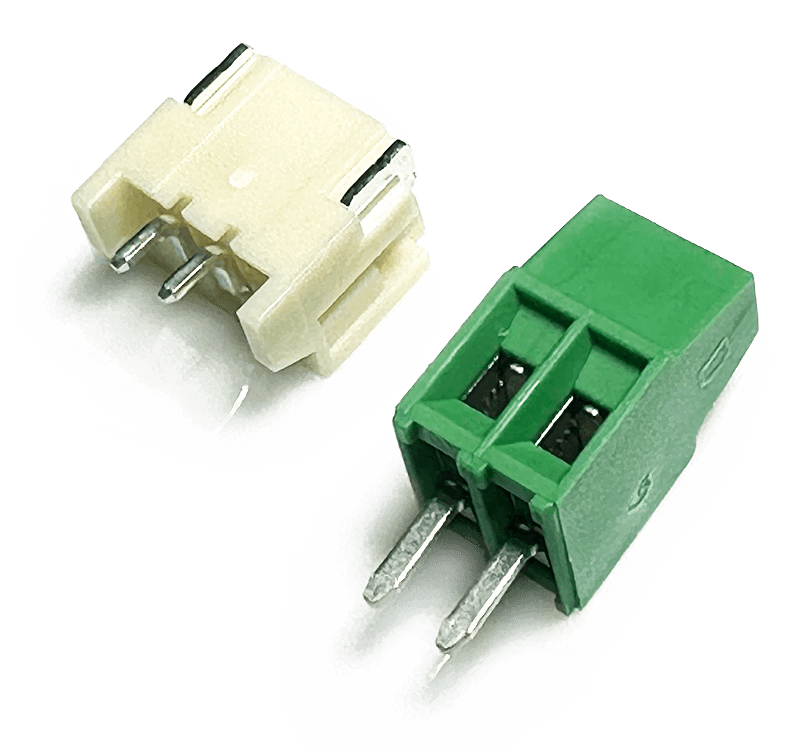
- The JST PH 2 connector (left) can soldered to the bottom of the board for battery connections.
- The terminal block (right) can be soldered to the SPKR pins for speaker wire connections.
- (not included) 2.54mm headers can be soldered to the GPIO + power pins for easy prototyping.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
ESP32-S3 | Microcontroller with WiFi and BLE |
GPIO | General Purpose Input/Output |
ADC | Analog-to-Digital Converter (audio input) |
DAC | Digital-to-Analog Converter (audio output) |
Battery Charging | Supports 3.7V LiPo/Li-Ion batteries |
USB-C | Interface for power and programming |
Audio In/Out Jack | Accepts a 3.5mm TRRS cable (mono in, stereo out) |
Speaker Amp | Can drive a small 4Ω speaker connected to SPKR pins (or optional terminal block) |
microSD Card Slot | Read/write access to microSD card using SPI interface |
Reset Button | Resets the ESP32-S3 microcontroller |
Power LED | Green LED indicates the board has power |
Programmable LED | Blue LED can be controlled by software |
Charge Status LED | Red LED indicates battery charging status |
Mic Preamp Gain | Clockwise rotation increases mic gain |
Level Selection | Switch #1: Input Level (OFF=Line, ON=Mic) |
Speaker Volume | Clockwise rotation increases speaker volume |
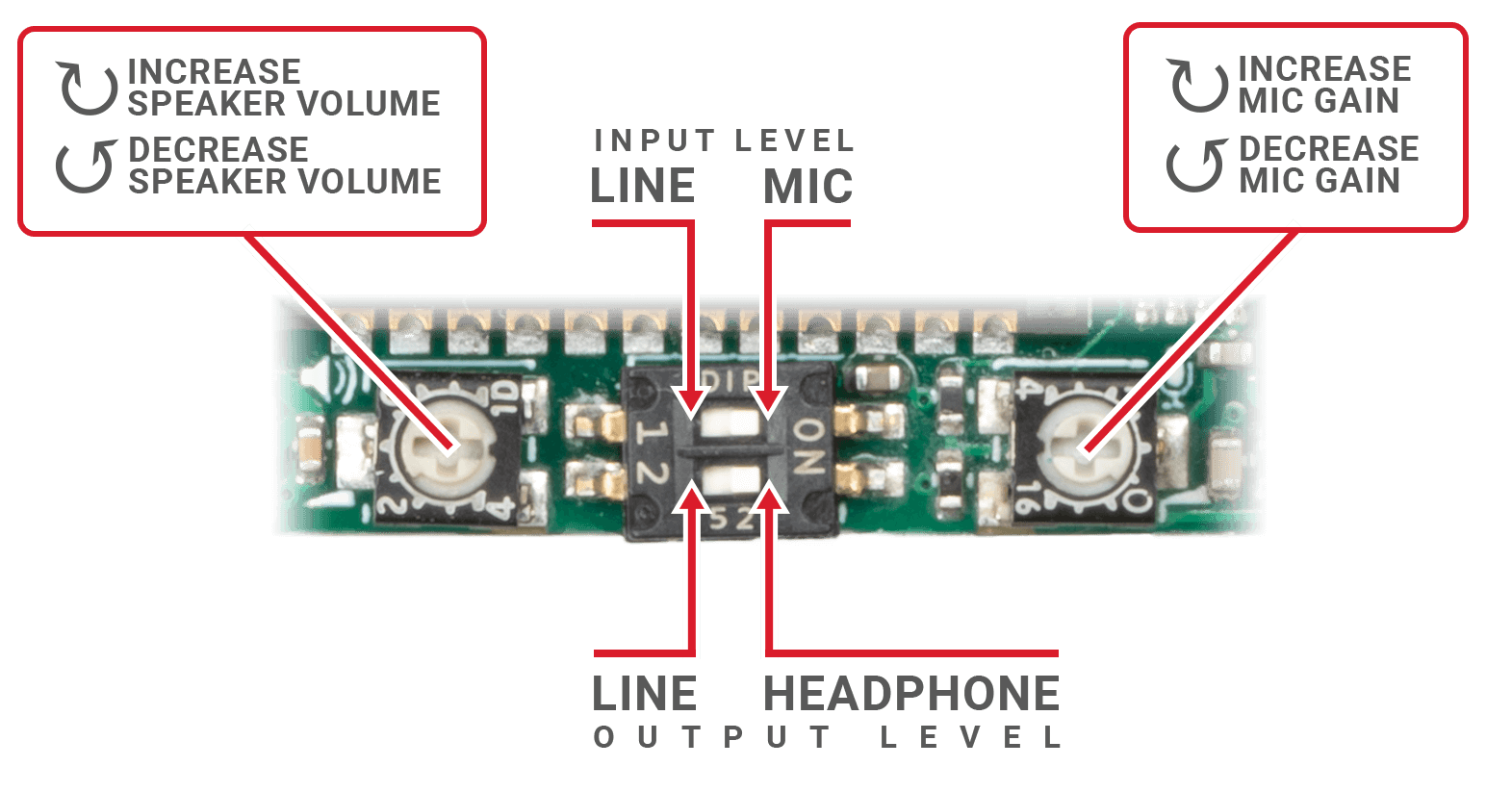
- Use a small screwdriver or paperclip to carefully adjust the level selection DIP switches as needed.
- The speaker volume and mic gain controls are adjustable with a small phillips or flat head screwdriver. Do not turn with excessive force; the trimpots are fragile and only have 250° of rotation from minimum to maximum.
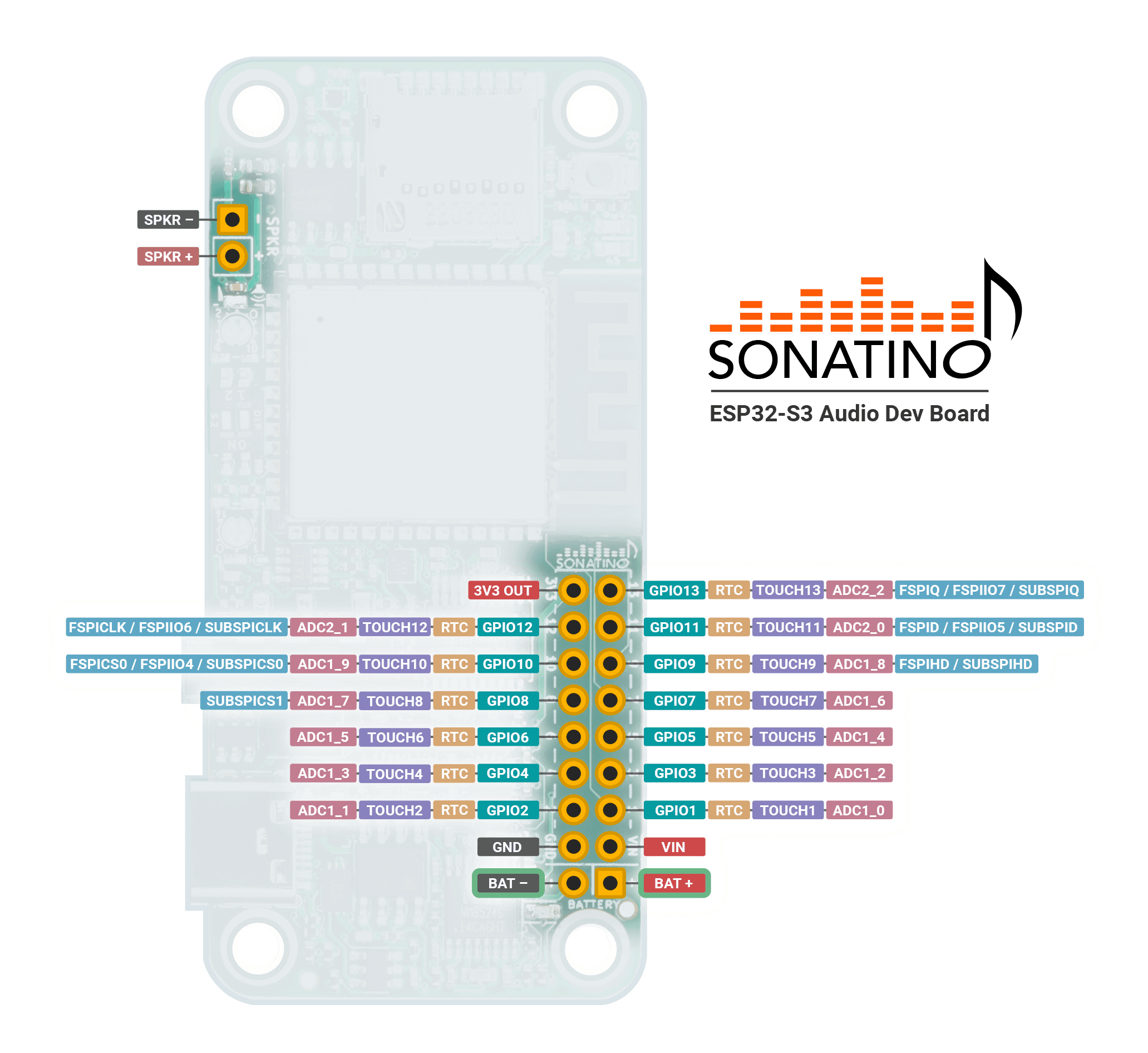
Pinout
| Pin | Component | Function |
|---|---|---|
VIN | Power | Power Input Positive (+) 3.3V - 5V (note) |
3V3 | Power | 3.3V Output (Regulated) (note) |
Battery- | Power | Battery Negative (-) |
Battery+ | Power | Battery Positive (+) 5V Max |
GND | Power | Ground |
GPIO 0 | Boot / MCLK | Boot / MCLK |
GPIO 1-13 | GPIO | General Purpose I/O |
GPIO 14 | DAC | Mute (Active LOW) |
GPIO 15 | DAC | BCLK / SCK |
GPIO 16 | DAC | LRCLK / WS |
GPIO 17 | DAC | Data (Out) |
GPIO 18 | ADC | Sample Rate (note) |
GPIO 21 | ADC | Bit Depth (note) |
GPIO 38 | ADC | BCLK / SCK |
GPIO 39 | ADC | LRCLK / WS |
GPIO 40 | ADC | Data (In) |
GPIO 41 | microSD (SPI) | D3 / CS / SS |
GPIO 42 | microSD (SPI) | CLK / SCK |
GPIO 43 | microSD (SPI) | CMD / SI / MOSI |
GPIO 44 | microSD (SPI) | D0 / SO / MISO |
GPIO 45 | LED | Blue LED |
GPIO 46 | All Amps | Amp Shutdown (Active LOW) |
GPIO 47 | Headphone Amp | Gain 0 (note) |
GPIO 48 | Headphone Amp | Gain 1 (note) |
SPKR + | 2.5W Amp | Speaker Positive (+) |
SPKR - | 2.5W Amp | Speaker Negative (-) |
Technical Details
Power
- Do not attempt to power the board using the 3V3 output pin. This pin is intended for powering 3.3V peripherals (generally around 400mA max) using Sonatino's onboard regulator. Connecting a power source to this pin may damage the board.
- If you power Sonatino using the VIN pin, DO NOT connect a battery or USB-C to the board. Charging only works with USB-C, and VIN should never be used with another power source connected at the same time.
- Sonatino can draw significant current at times (depending on usage; can be 1A or more). If your power source cannot supply enough current, you may experience unexpected behavior.
- The charging circuit is configured to deliver up to 500mA of current to a battery. Please check that your battery can handle this charging rate, especially for batteries with less than 500mAh of capacity.
- A few ways to reduce power consumption and extend battery life:
- Turn off wireless functions on the ESP32-S3 when not in use.
- Configure the ESP32-S3 to use a lower CPU frequency or dynamic frequency scaling (DFS).
- Set GPIO 46 to LOW: this shuts down the 2.5W amp, headphone amp, and microphone preamp.
- Set GPIO 14 to LOW to mute the DAC.
- Stop outputting a MCLK signal on the ESP32-S3's GPIO 0 (may require calling i2s_stop()). This will power down the ADC and DAC.
- Put the ESP32-S3 into light sleep or deep sleep (esp_light_sleep_start() or esp_deep_sleep_start()). If you've shut down the amps by setting GPIO 46 to LOW, don't forget to call gpio_deep_sleep_hold_en() before sleeping to keep the pin held low.
- Remove any microSD card if you aren't using it.
- You can disable the green power LED by carefully cutting the trace between the two jumper pads of JP1 on the underside of the board.
Programming
- Sonatino can be programmed using a number of different software tools. While Arduino IDE is probably the easiest for getting started, PlatformIO and ESP-IDF offer some additional benefits for more advanced projects.
- When uploading code, Arduino IDE will usually take care of putting the board into flashing mode and then resetting the board when the upload is complete. If that doesn't work, check that the correct port and board is selected, then try again. Some development tools don't handle the flashing process correctly by default, so you may need to adjust your software's board settings.
- In rare cases, you may need to manually put the board into flashing mode. This can be done two different ways, depending on your board revision (found on the underside of the board, near the right-hand edge — looks like "rev x.x.x"):
- Rev 2.6.1 and above: Hold down the "BOOT" button, and while holding it down press and release the "RST" button. Then release the "BOOT" button.
- Rev 2.5.x: Temporarily short (e.g., with a short length of wire) the "MCLK/0" pad on the underside of the board with GND. While doing that, press and release the reset button ("RST") on the front and remove the wire.
Audio
- Sonatino uses separate bit clock (BCLK) and word clock (LRCLK) lines for the DAC and ADC — as noted in the pinout. The ESP32-S3 supports two I2S ports, so you can configure and use the DAC and ADC simultaneously (technically they could share those lines, but Sonatino wires them separately for added flexibility).
- GPIO 18 and GPIO 21 are connected to FSAMPEN and IWL pins of the WM8782 (ADC), respectively. These pins are used to configure the ADC's sample rate and word length. See the WM8782 datasheet for more information.
- GPIO 47 and GPIO 48 are connected to GAIN0 and GAIN1 of the TPA6132A2 (Headphone Amp), respectively. The default state corresponds to 0 dB gain (GAIN0 is pulled HIGH and GAIN1 is pulled LOW), but can be set to -6 dB, 0dB, 3dB, or 6 dB based on pin state. See section 7.4.1 of the TPA6132A2 datasheet for more information.
- The 2.5W mono amplifier is connected to the left output channel.
- Without properly setting volume/gain (in software and hardware), audio output from Sonatino can be very loud! It can also become distorted if the volume is set too high. Please protect your ears and be careful when testing audio output!
- Crackling, stuttering, or choppy audio is most often caused by misconfigured settings (sample rate, word length, master clock, DMA buffer, etc.) or by delays in the audio processing pipeline. Double-check that all your settings are correct and that no time-consuming tasks are blocking the delivery of audio samples. You may need to use RTOS programming to take advantage of both cores of the ESP32-S3.
Cases / Enclosures
- Sonatino will fit into some cases designed for the Raspberry Pi Zero, but not all. Cases that are open around the edges of the board generally work without modification, but those with cutouts for ports on the Raspberry Pi Zero (including the official case sold by Raspberry Pi) won't match the ports on Sonatino. Often, those cases can be modified by expanding or cutting out new holes for Sonatino's ports.
Datasheets
Microcontroller
DAC
ADC
Stereo Headphone Amplifier
2.5W Amplifier
Microphone Preamplifier
Battery Charger
Specifications
Microcontroller & Storage
- Microcontroller: ESP32-S3-WROOM-1 with 16 MB flash and 8 MB PSRAM (previously 2 MB PSRAM)
- Additional Storage: microSD card slot with SPI interface
Audio
- DAC: Cirrus Logic WM8524 — up to 24-bit 192kHz output (stereo)
- ADC: Cirrus Logic WM8782 — up to 24-bit 192kHz input (mono)
- Audio format: I2S
- Speaker Amp: PAM8302 — 2.5W @ 4Ω (mono) with adjustable volume
- Interface: 3.5mm audio jack supporting input and output (TRRS, CTIA standard)
- Stereo Headphone Amp: TPA6132A2
- Microphone Preamp: MAX4467
- Input Level: Mic or line level
- Output Level: Line or headphone level
- Speaker Connection: onboard pins, optional screw terminal
Connectivity
- WiFi: 802.11 b/g/n
- Bluetooth: 5.0 (LE)
- GPIO: 13 general-purpose I/O pins
- USB-C for programming and data I/O
Power
- Power Source: USB-C, 3.7V LiPo/Li-Ion battery, or 5V DC
- Battery Charging: Charging circuit with overcharge and over-discharge protection
- Low-Power Mode: ESP32-S3 supports deep sleep, and audio components can be put into low-power mode to extend battery life
- Battery Connection: onboard pins, optional JST PH 2 battery connector (check polarity before connecting)
Status and Control
- Trim pots for adjusting speaker volume and mic gain
- Dip switches for selecting mic/line level and line/headphone level
- Reset button
- User-programmable blue status LED
- Power and battery charging status LEDs
Physical
- Dimensions: 65 x 30 mm x 7mm (2.6 x 1.2 x 0.3 in)
- Weight: 11 g (0.4 oz)
- Same size as a Raspberry Pi Zero (not compatible with Pi Zero)
- Can be used with some Pi Zero cases (may require case modification)
Additional Resources
Inter-IC Sound (I2S) — Espressif API reference for I2S audio on ESP32-S3
ESP-ADF — Espressif Audio Development Framework
ESP-Skainet — Voice assistant / speech recognition for ESP32-S3
ESP8266Audio — Arduino library for playing audio on ESP8266 and ESP32
pschatzmann/arduino-audio-tools — Arduino Audio Tools
esp32_basic_synth — ESP32 based simple synthesizer project